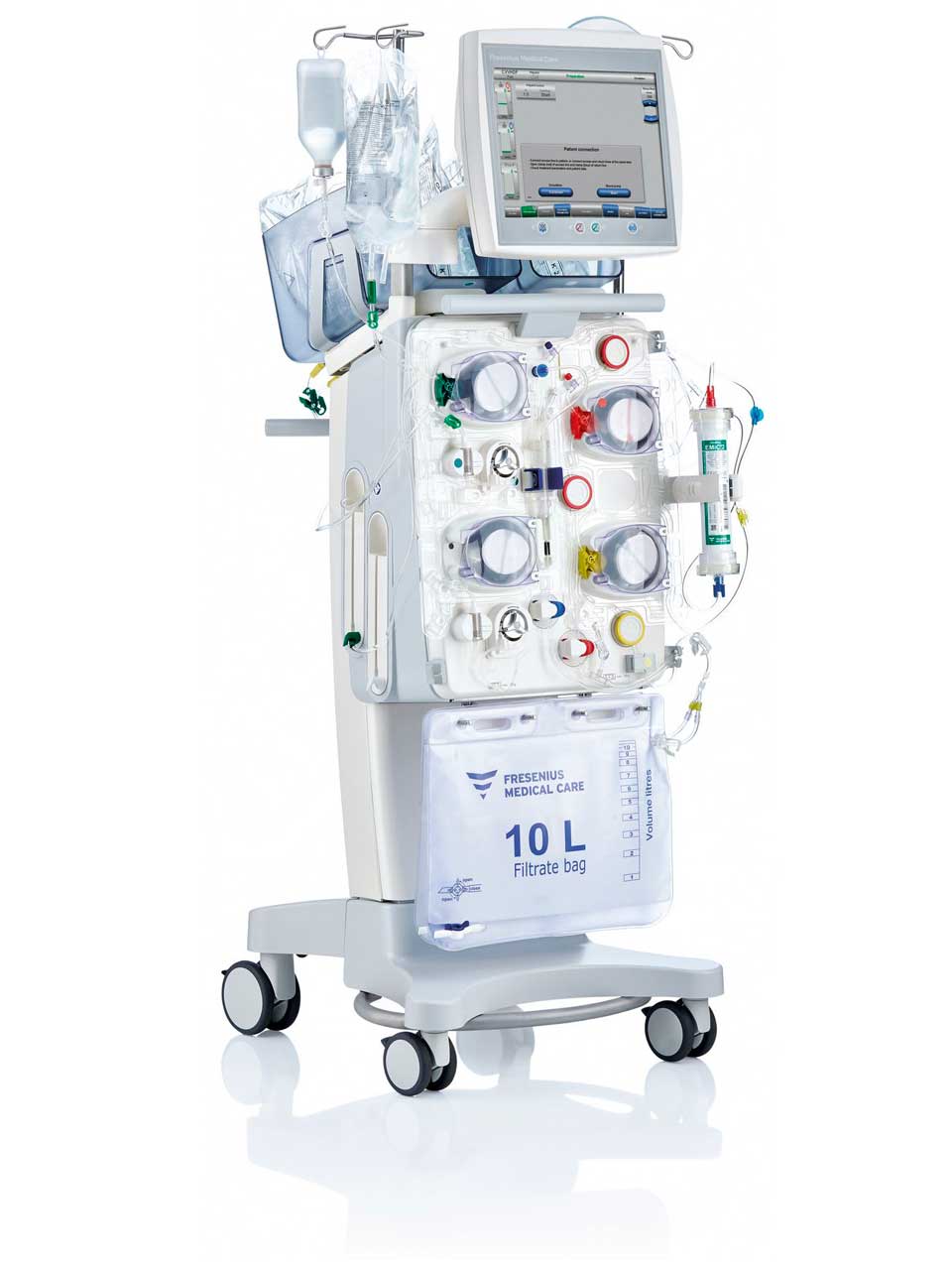
multiFiltratePRO

A perfect fit for every team
- CRRT with integrated Ci-Ca® anticoagulation – safe and efficient
- Allows therapy diversity with Therapeutic Plasma Exchange and sepsis therapy
- Convenient handling, easing daily routines
Key features at a glance
| multiFiltratePRO acute therapy options |
|
| Ergonomic design |
|
| Easy treatment application |
|
| Comprehensive integrated Ci-Ca anticoagulation |
|
multiFiltratePRO Ci-Ca
Integrated Ci-Ca® citrate anticoagulation
Statement on the Ci-Ca® protocol:
[It] enabled an effective treatment of acute renal failure and excellent control on the acid–base status as well on the systemic ionised calcium in combination with negligible clotting issues.2
Intelligent software support
Coupling of all active pumps through a single user interface:
- Infused volumes of citrate and calcium solutions are automatically balanced with the filtrate pump
- If the blood flow is changed, the device automatically adjusts the citrate pump
- If the filtrate flow is changed, the calcium pump is adjusted accordingly
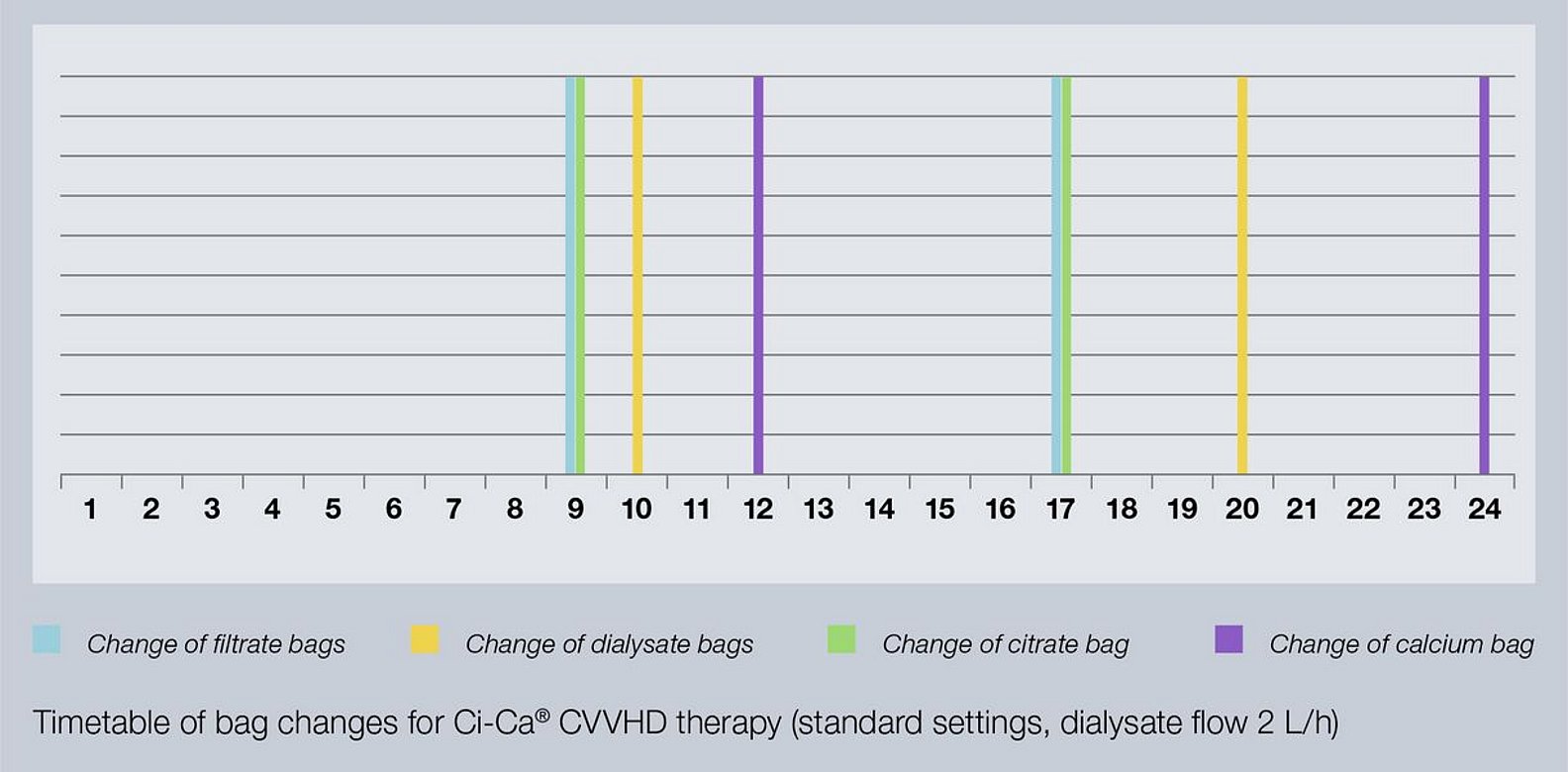
- The citrate infusion continues for a reliable, limited period of time throughout bag changes (dialysate, substituate, filtrate). This helps to avoid an early coagulation of the system.
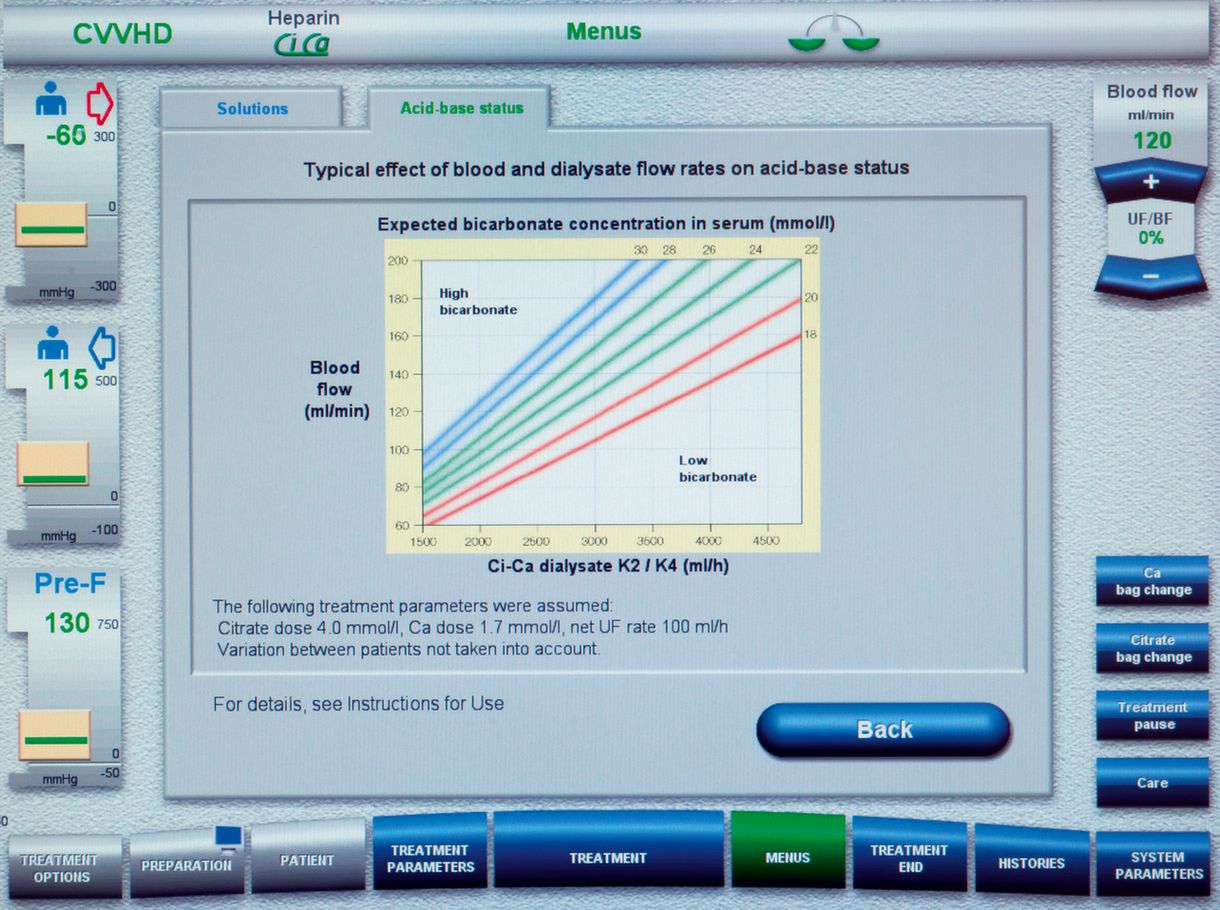
Screen during Ci-Ca® CVVHD application provides key information from the Ci-Ca® protocol
Ci-Ca® protocol included in the software
For routine adjustments of the Ci-Ca® therapy, information from the protocol can easily be retrieved on the screen
In case of certain values set outside the standard range, the multiFiltratePRO makes the user aware of potentially risky clinical situations

Nurse operating multiFiltratePRO device
Dedicated hardware components for citrate anticoagulation
Dedicated pumps for citrate and calcium keep the syringe pump available for heparin application if needed during Ci-Ca® therapy. Separate level detectors and drip counters enable timely detection of empty bags, preventing air being transported downstream and enabling a smooth continuation of the treatment. During bag changes (dialysate, substituate, filtrate) the citrate infusion continues for a reliable period of time. This helps to avoid early coagulation of the system
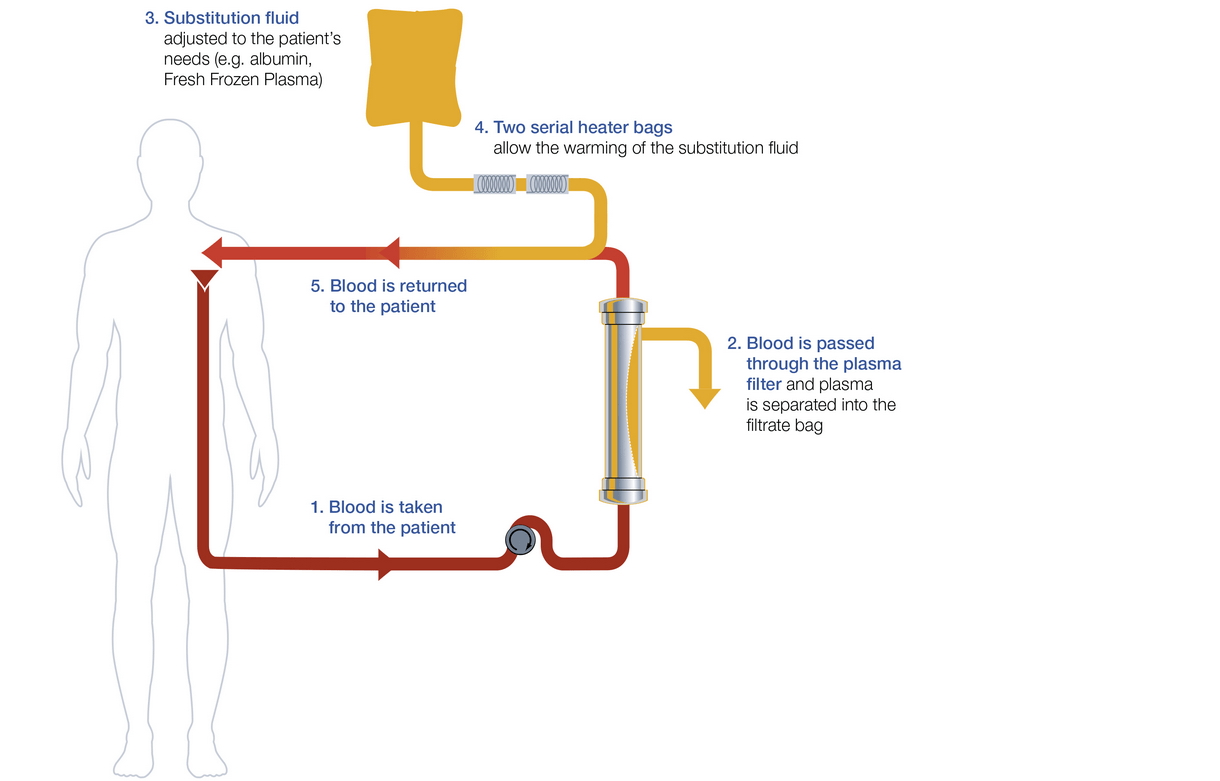
Therapeutic plasma exchange
Therapeutic plasma exchange is a well-established extracorporeal blood purification technique.
As described by Reeves et al., “the therapeutic effects of TPE could include the removal of pathological substances from the blood, such as monoclonal paraproteins and autoantibodies, as well as the replacement of deficient plasma components when plasma is used as a replacement fluid.”5
Indications for TPE cover selected diagnoses from different specialties:5
- Neurology
- Hematoloy
- Rheumatology
- Nephrology
In contrast to separation via centrifugation, multiFiltratePRO separates the plasma from the blood cells via membrane plasma separation (MPS).
multiFiltratePRO TPE – Benefits at a glance
Easy set-up
Touchscreen-based interface guides the nurse through the entire setup, rinsing and priming.
Key information on the screen
Pressure display, exchanged volume and target plasma volume, treatment time, flow rates and pressure history.
Integrated automated plasma volume calculation
The patient’s plasma volume and the respective plasma exchange volume can be calculated by the plasma calculator of the multiFiltratePRO, according to Sprenger et al.6
Substitution fluid holder
Placed on the upper scale tray, the substitution fluid holder allows for easy bottle and bag handling at eye-level.
Two integrated substitution fluid heater bags
Two integrated substitution fluid heater bags gently warm the substitution solution to curtail the cooling of the patient.
Automated ramp-up of plasma separation
The multiFiltratePRO features a plasma to blood ratio ramp-up procedure to provide for a smooth start of plasma separation and stable filtration conditions7, while saving the user time, see figure 1: Plasma to blood ratio ramp-up.
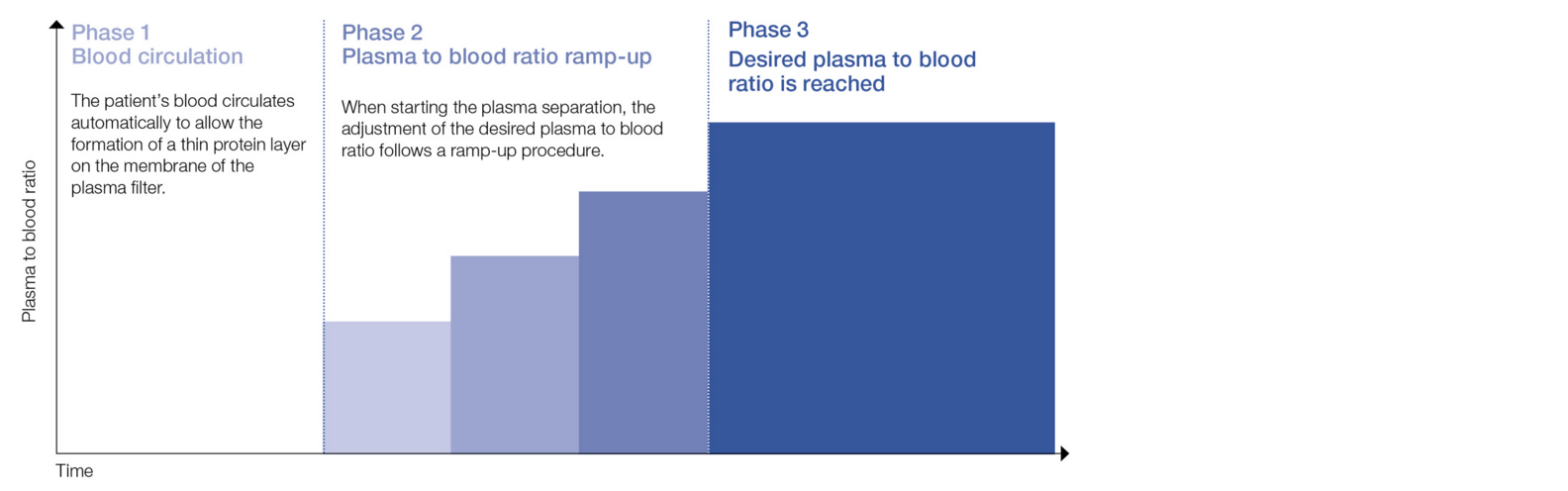
Figure 1: Plasma to blood ratio ramp-up
Convenient handling
Large and adjustable monitor
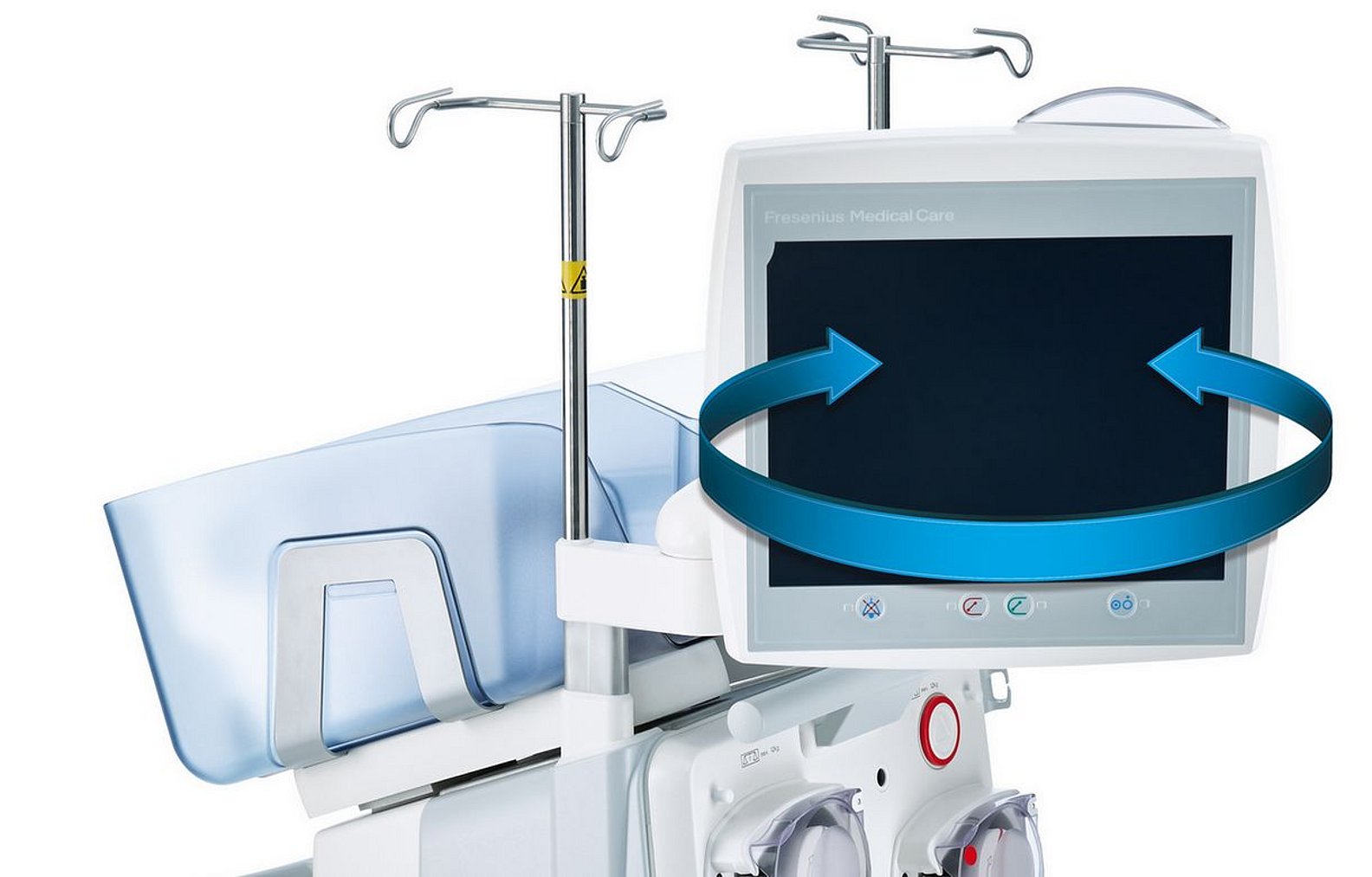
multiFiltratePRO monitor (front)
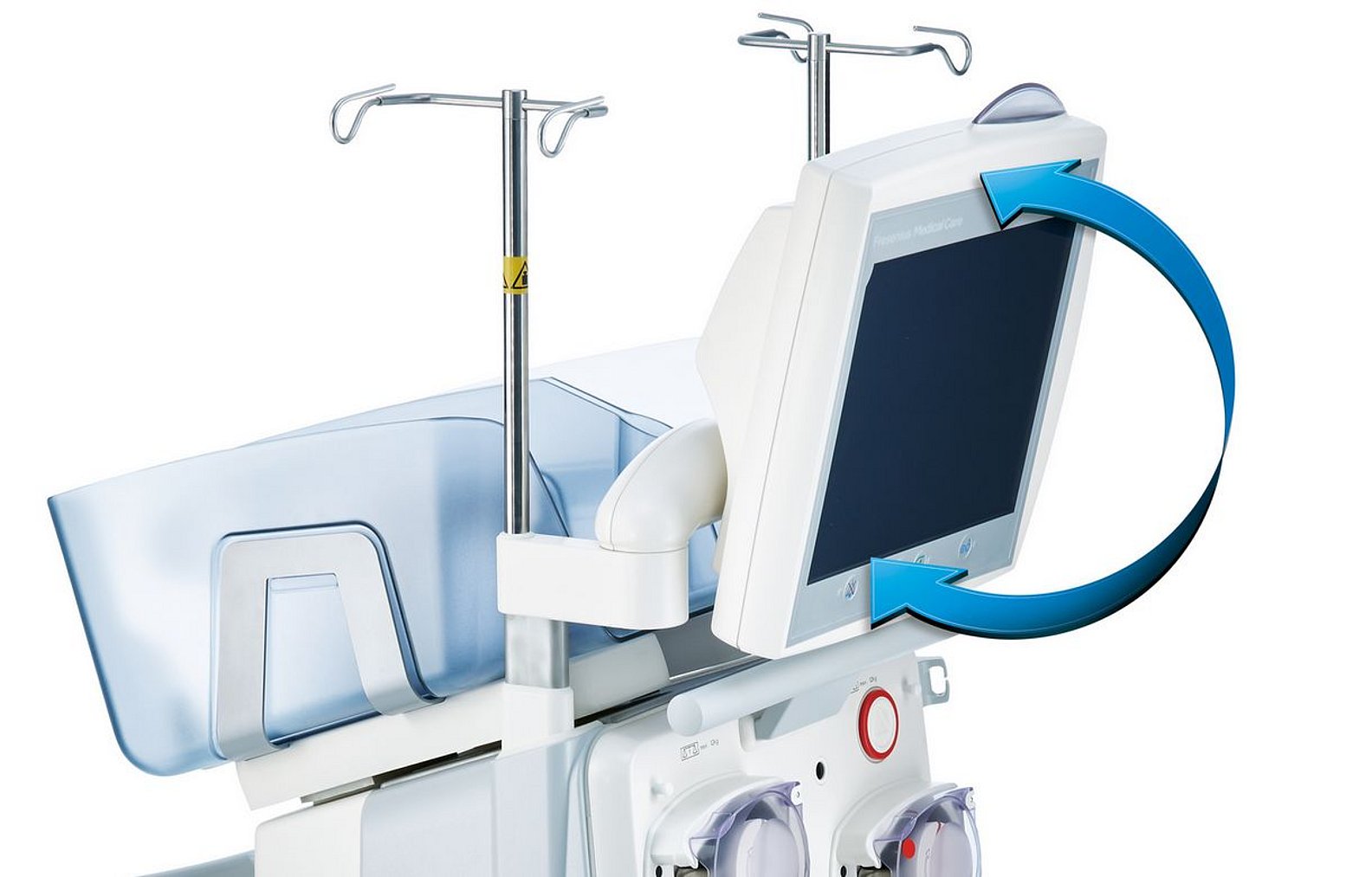
multiFiltratePRO monitor (side)
The easy-to-read touch screen monitor allows recognition of key information even from a distance. Rotation around the horizontal and vertical axes enables adjustment for different-sized users and to different relative positions of the device and user.
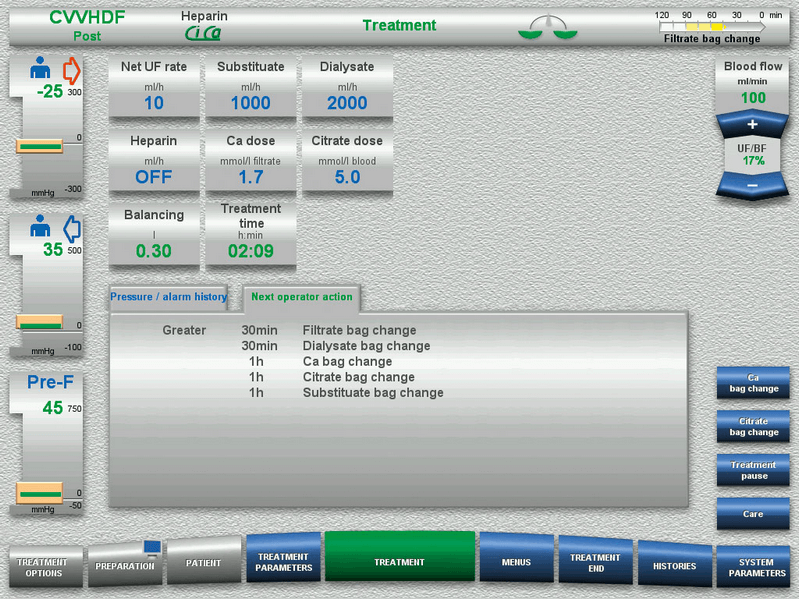
multiFiltratePRO interface
Advanced graphic user interface
The multiFiltratePRO includes a graphic user interface that monitors and displays all relevant set-up and treatment data. The integrated alarm system helps to quickly determine the urgency as well as the root cause of alarms.
The time until the next expected user action is displayed in the status bar at the top right of the screen. In addition, a list of further upcoming user interactions can be retrieved on the screen. Both help to optimize work processes in the ICU.
The “Care Button” switches the multiFiltratePRO into care-mode, by decreasing the blood flow, stopping the balancing system and extending the pressure limits. This will prevent unnecessary alarms when moving the patient or manipulating the catheter.
Easy application of CRRT
Device-supported set-up process
Long intervals between bag changes
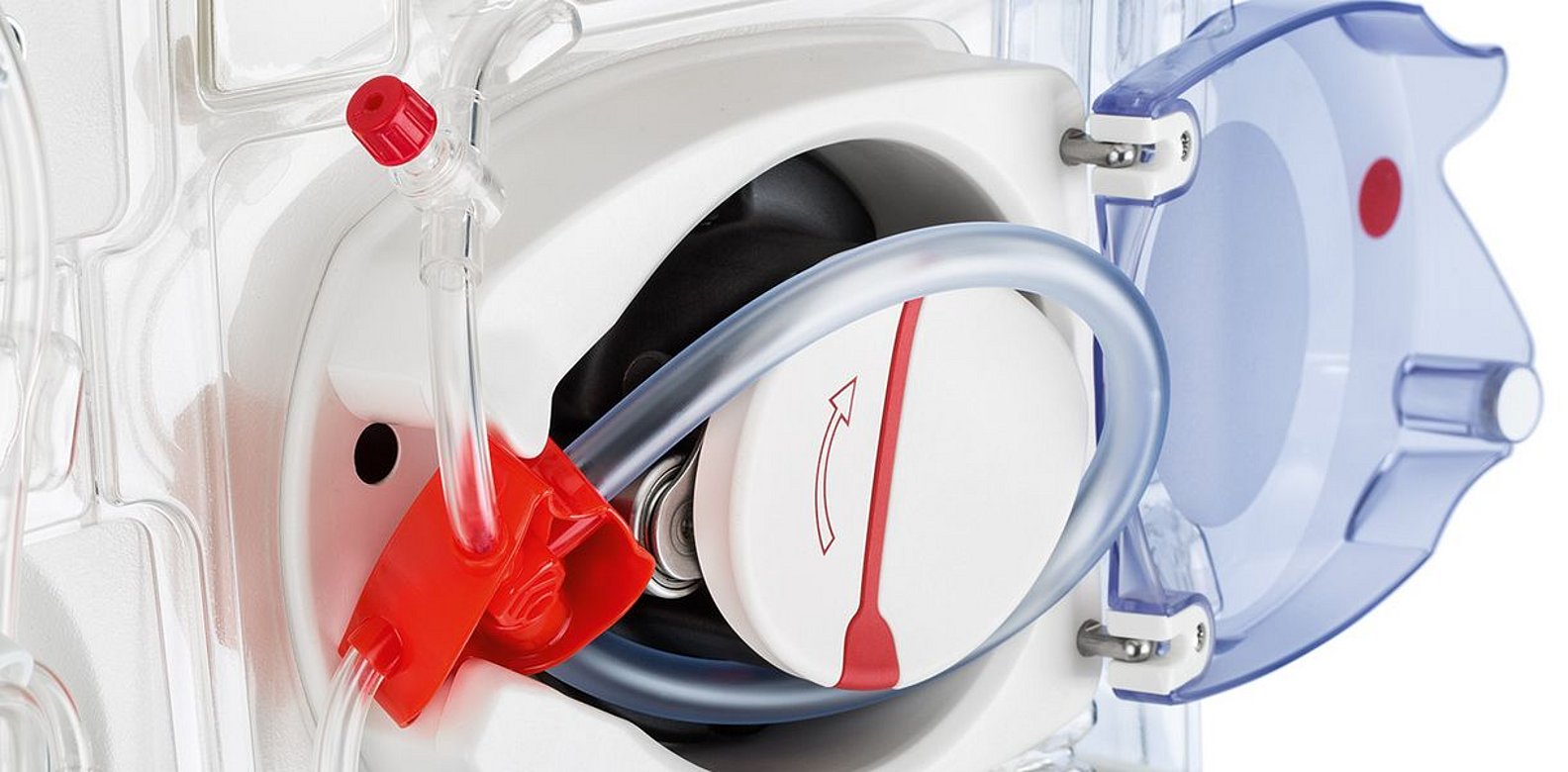
multiFiltratePRO blood pump: Fitting the pump positioners automatically triggers the insertion of the pump segment. The corresponding pressure domes open and guide the correct installation of the tubing. Multiple automated tests accompany the set-up process, keeping the user on the right track. As a result, the number of handling steps is reduced.
1 KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney International Supplements 2012. 2:1-138.
2 Morgera S et al., A safe citrate anticoagulation protocol with variable treatment efficacy and excellent control of the acid-base status. Critical Care Medicine 2009. 37:2018-24.
3 Morgera S et al., Metabolic complications during regional citrate anticoagulation in continuous venovenous hemodialysis: single-center experience. Nephron Clinical Practice 2004. 97:c131-6.
4 Kalb R et al., Regional citrate anticoagulation for high volume continuous venovenous hemodialysis in surgical patients with high bleeding risk. Therapeutic Apheresis and Dialysis 2013. 17:202-12.
5 Reeves HM et al. The mechanisms of action of plasma exchange. British Journal of Haematology 2014;164(3):342-51.
6 Sprenger KB et al. Nomograms for the prediction of patient’s plasma volume in plasma exchange therapy from height, weight, and hematocrit. Journal of Clinical Apheresis 1987;3(3):185-90.
7 Malchesky PS Membrane processes for plasma separation and plasma fractionation: guiding principles for clinical use. Therapeutic Apheresis 2001;5(4):270–282.